Access, Roles, and Permissions¶
Alation Cloud Service Applies to Alation Cloud Service instances of Alation
Customer Managed Applies to customer-managed instances of Alation
Roles, permissions, and various access rules usually define what a user is allowed or denied in a software product. In Alation, there are several factors that control what you can see and what you can do in the Catalog.
Access to Functionality¶
To control access to functionality, Alation has roles. To control access to Catalog objects, there are privacy settings applicable to specific objects or inherited from the source database or BI platform. There are also custom field permissions that define a user’s ability to edit custom fields. Field permissions can be applied to individual users or groups.
When you first join Alation, you are assigned a user role. There are seven roles, as described in Roles Overview.
Your user role is the primary access rule that determines what pages you see in the Catalog and what actions you can perform. For example, as a Server Admin, you will be able to access the Admin Settings page, which other roles cannot do. As a Catalog Admin, you can create and manage Catalog sets and custom field permissions, which a Viewer cannot do. If an action in Alation is not allowed because your role does not grant permission for it, certain parts of the interface will appear inactive and you will see an insufficient permissions message on hover-over.
Access to Objects¶
Access to Articles¶
Articles have access settings of their own. You can make your article private and not findable by other users in Search; you can share it with specific users or keep it public and accessible by everyone in Alation. Your ability to find and read an article in your Catalog depends on the access settings for this specific article, as described in Sharing and Access.
Access to BI Objects¶
For BI sources in Alation (for example, Tableau sources), Alation will attempt to establish a match between Alation users and the BI system users so that the view permissions for extracted BI objects can be extracted into Alation too. If Alation cannot find a BI user match for an Alation user, this user will not be able to view the extracted BI objects. For more information about permission mirroring for BI sources, see, for example, Permission Mirroring for Tableau.
Access to Data Sources and File Systems¶
Access to data sources and file systems can be controlled for each individual source and granted to individual users. Whether or not you can view a data source or a file system source in Alation depends on their visibility settings.
Data sources and file system sources can be public (visible to everyone) or private (visible only to users who were granted access).
To be able to work with the settings of a data source and run the data jobs you must be granted the Data Source Admin function for a given data source.
See Access Tab for more details about access settings of data sources.
To be able to work with the settings of a file system source, you must be granted the File System Admin function. Privacy settings of file systems are available from version 5.12.3. Refer to Access to File Systems for more details.
Access to Document Hubs, Folders, and Documents¶
Document hubs are always visible to all users of the catalog, as long as they are published. By default, folders and documents are accessible to everyone, but you can limit access if desired. Documents inherit permissions from their parent folder by default. You can control access to a folder and all its documents by setting permissions on the folder. You can also set permissions on each document individually. Document permissions override folder permissions. See Document Hub Permissions for more details.
Access to Glossaries and Terms¶
The Glossary Hub is always visible to all users of the catalog. By default, glossaries and terms are accessible to everyone. Terms inherit permissions from their parent glossary by default. You can control access to a glossary and all its terms by setting permissions on the glossary. You can also set permissions on each term individually. Term permissions override glossary permissions. See Glossary Permissions for more details.
Access to Queries¶
Query objects have access settings too. The way query access works changed significantly in 2023.1.
In 2023.1 and later, your access to a query is determined by a combination of whether you have access to the underlying data source and whether you have individual permission to the specific query. By default, queries can be viewed and run by anyone who has access to the relevant data source. Users with edit or owner access can grant permission to view, run, or edit a query for individual users and groups. Unpublished queries may be hidden, depending on your Alation configuration. See Share and Access Queries - 2023.1 and Later for more information.
In 2022.4 and earlier, your access to view and run a query depends primarily on whether you have access to the underlying data source. You can view any query for data sources you have access to using Search. If the Viewer role is not enforced, you can also run any query. You can view both published and unpublished queries by default. Unpublished queries may be hidden, depending on your Alation configuration. To edit a query, you need to explicitly request edit access to that query. See Share and Access Queries - 2022.4 and Earlier for more information.
Access to Tables¶
From release 2020.4, in the Alation Catalog, user access to Table objects can be controlled separately from access to the parent Data Source: permissions to view a table can be set for a specific table object. Users can only view the Table objects that they have the access permissions for. Table privacy can be enabled on your instance by a Server Admin. For details, see Table Privacy Settings.
Visibility Settings Using Manual Catalog Sets¶
Sometimes Catalog Admins may choose not to include specific data objects into Search results using visibility settings in manual Catalog sets. This is another reason why specific objects may be hidden from Search.
Access to Catalog Fields¶
Custom Field Permissions¶
Whether or not users can edit custom fields on data objects as part of the curation effort can be controlled with custom field permissions. If the editing capabilities on a field on a data object page appear disabled to you, this means field permissions are enforced and editing may only be allowed for a specific group of users.
Access to Data¶
Alation provides the ability to view a small sample of real data in the Catalog. This means Catalog users may see examples of real data on the respective pages of tables and columns under Samples.
There are several ways Data Source Admins can control access to data:
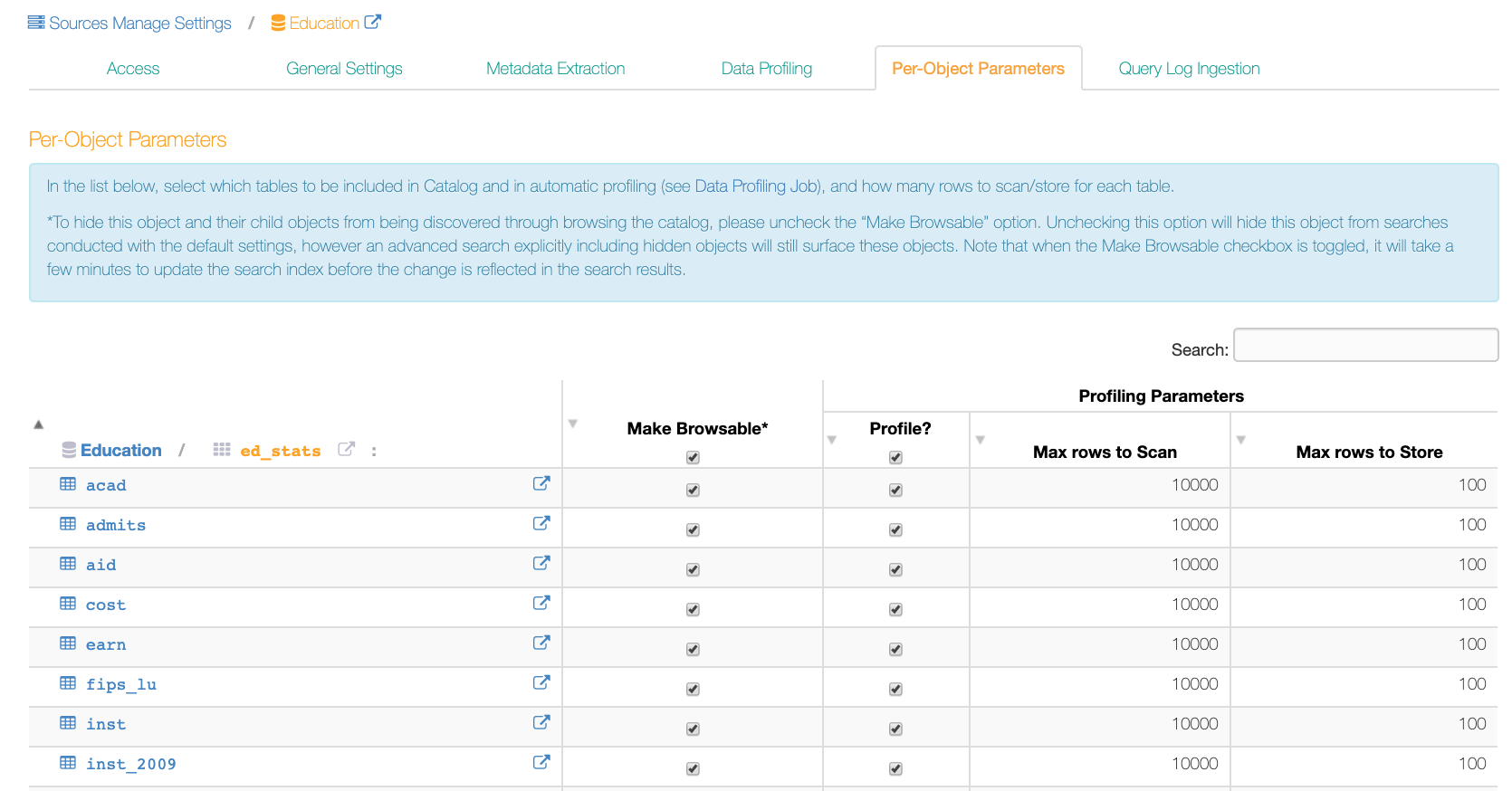
Per-Object Parameters¶
It is possible to specify which data objects should not be browsable using the Catalog Browser (the left-hand navigation panel) and should not be sampled. To do so, an admin can use the settings on the Per-Object Parameters tab of a data source settings page:
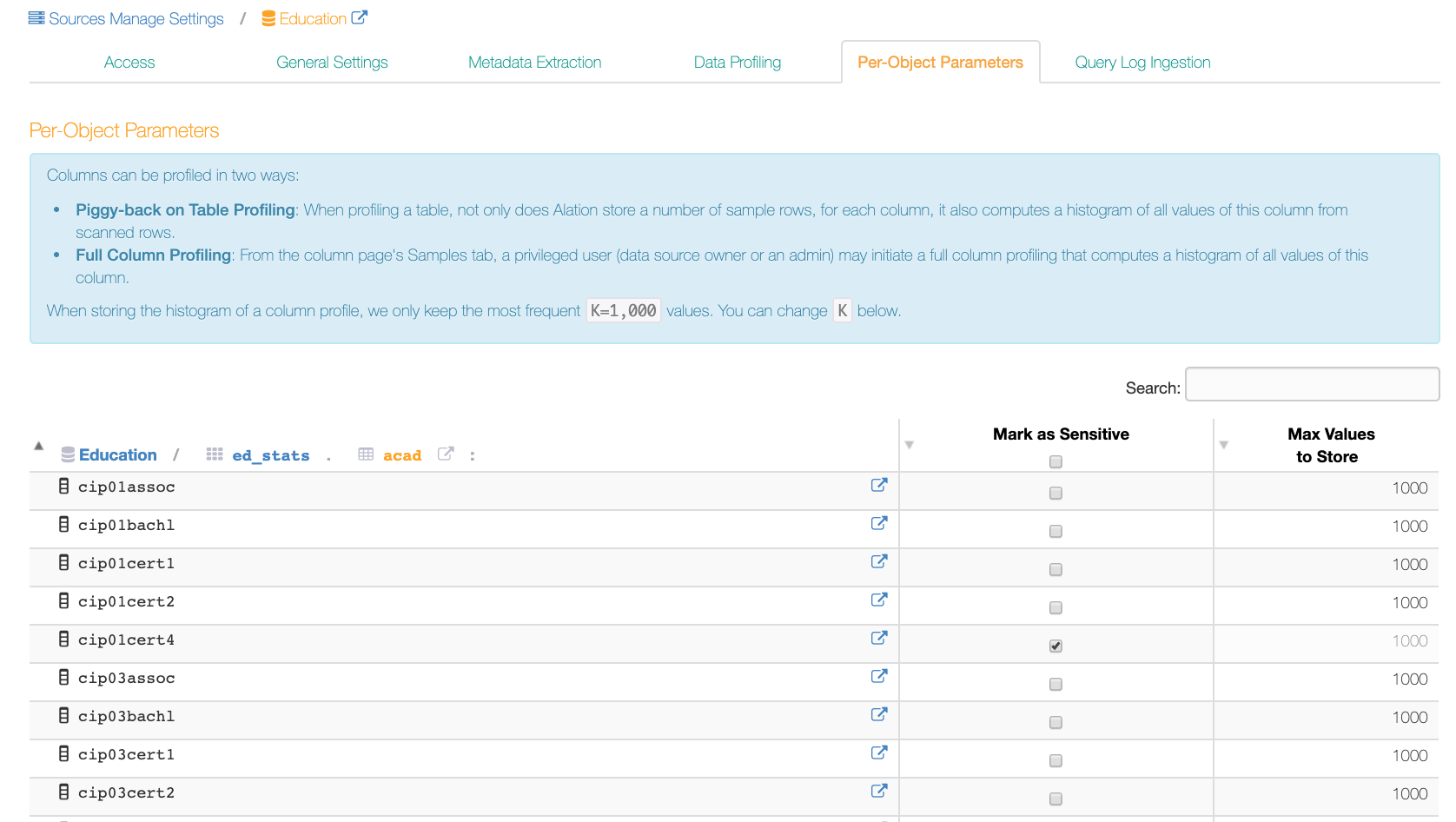
Sensitive Data Setting¶
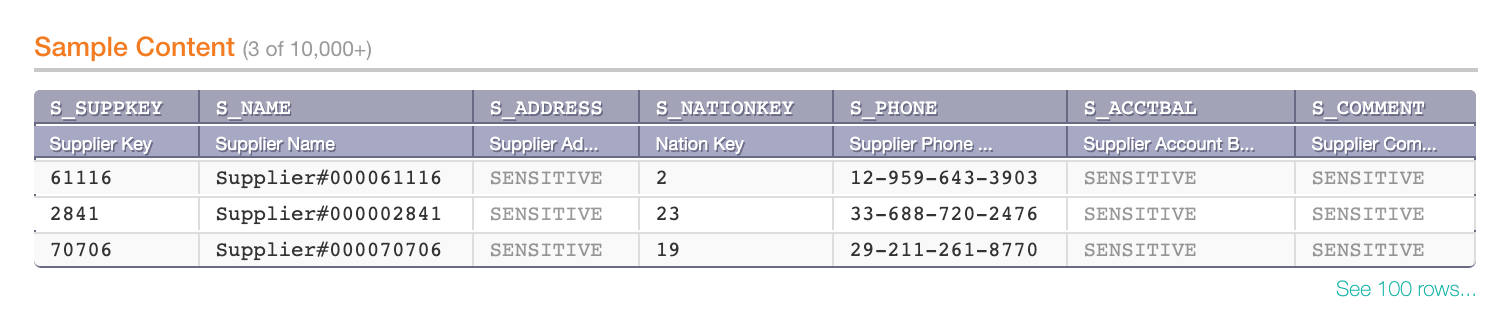
It is possible to mark data as sensitive on the column level, on the Per-Object Parameters tab. Values of sensitive columns will not be sampled:
Sensitive columns in the Sample Content table on a table object page:
Dynamic Profiling¶
An admin can turn on Dynamic Profiling on the General Settings tab of a data source settings to require users to enter their own credentials before they can run a table or a column profile. They will only be able to see the data they have access to on the database. Sample data will only be visible to the user who performs profiling:
For help working with credentials, see Working with Data Source Connections.
Obfuscate Literals¶
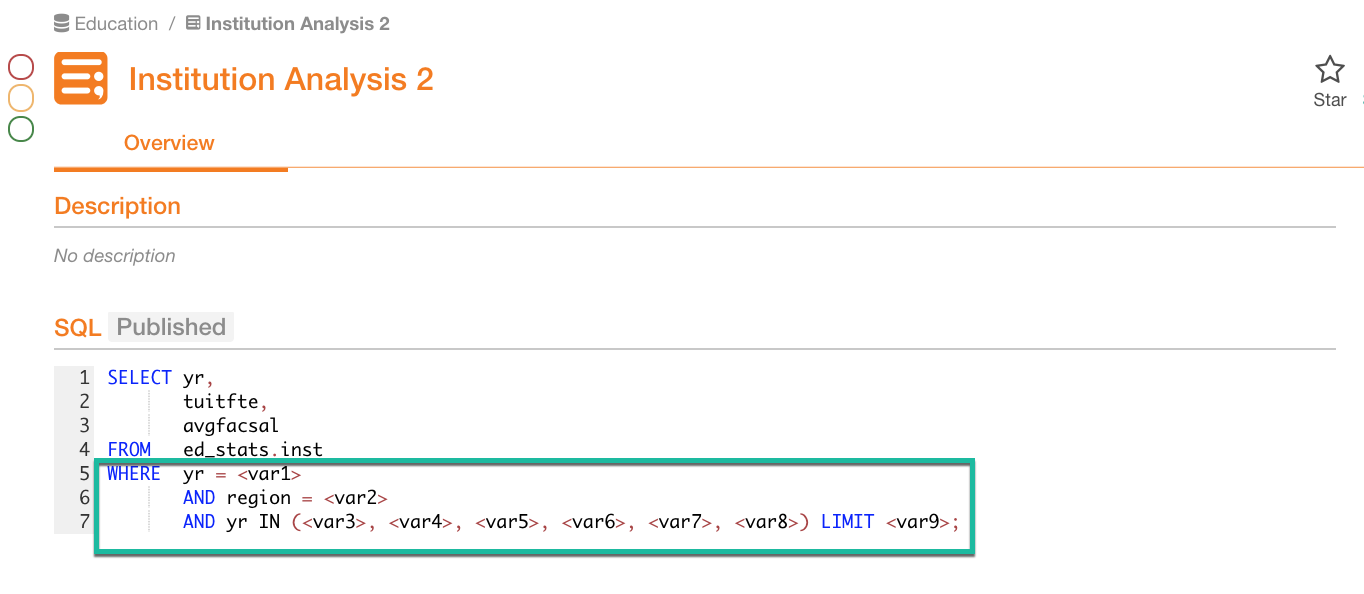
You can turn on Obfuscate Literals on the General Settings tab of a data source settings so that literal values in ingested queries are not shown in the UI. Instead, users will see placeholder values.
Obfuscate Literals OFF :
Obfuscate Literals ON :
Note
Starting in Alation version 2023.1.2, you will not see the SQL of the query if the SQL parser fails to process the query after obfuscation was turned on. In this case you will see a message warning you that the query cannot be displayed: This query cannot be displayed with current data source settings.
Access to Compose¶
In Compose, before users are able to run queries on a data source and retrieve any real data, they will need to authenticate with their database credentials:
This ensures that users only retrieve data they are granted access to on the database.